[09]
2025
Project
[Design]
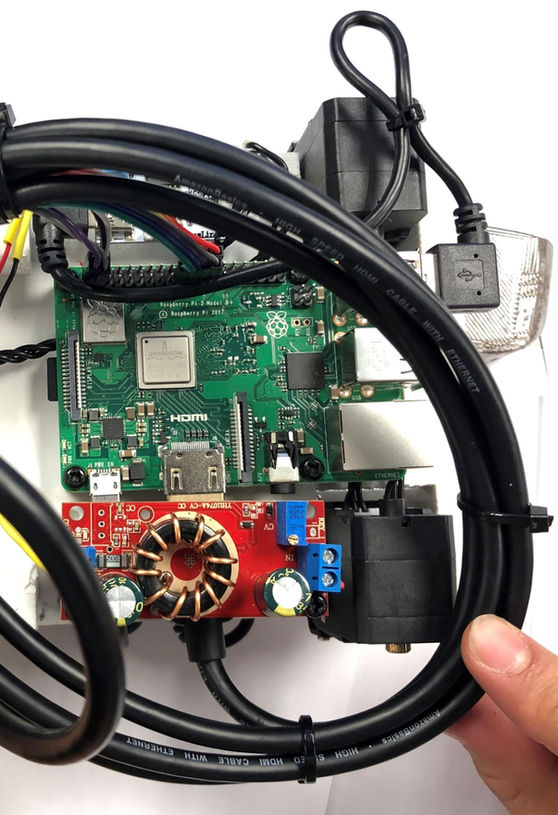
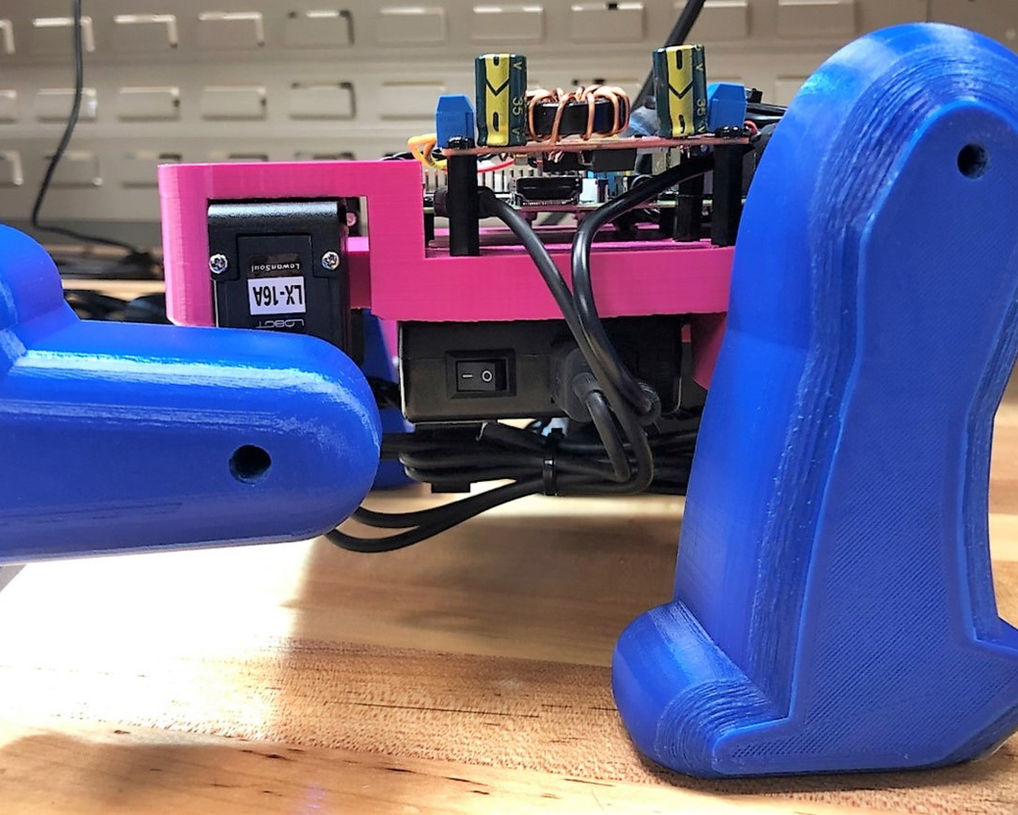
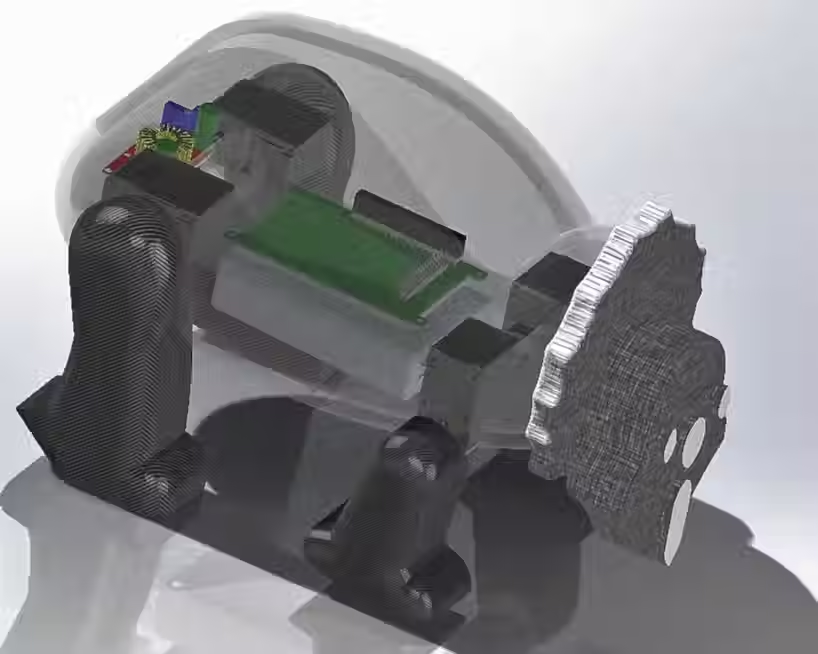
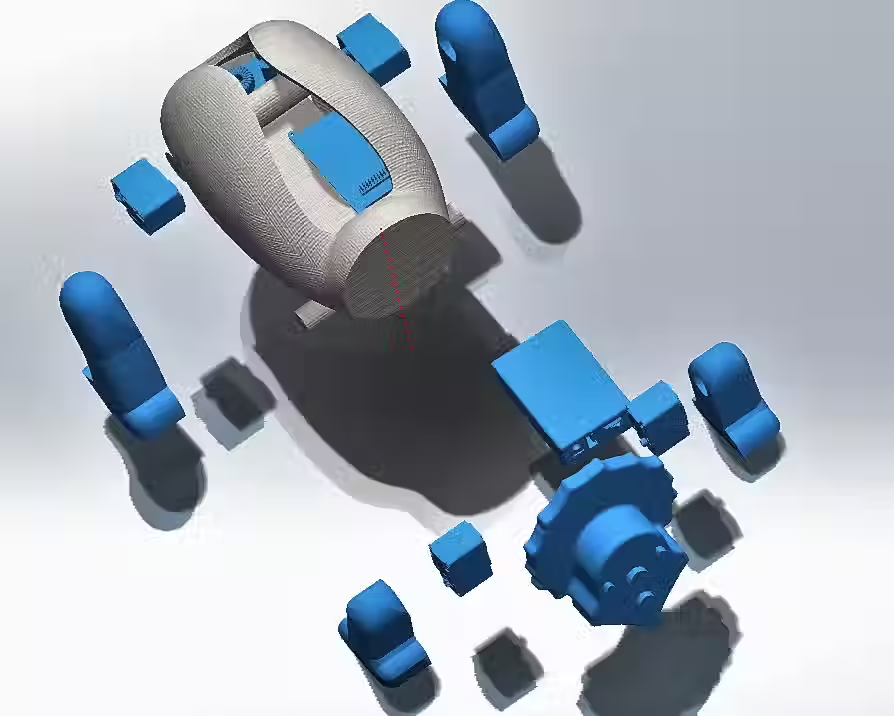
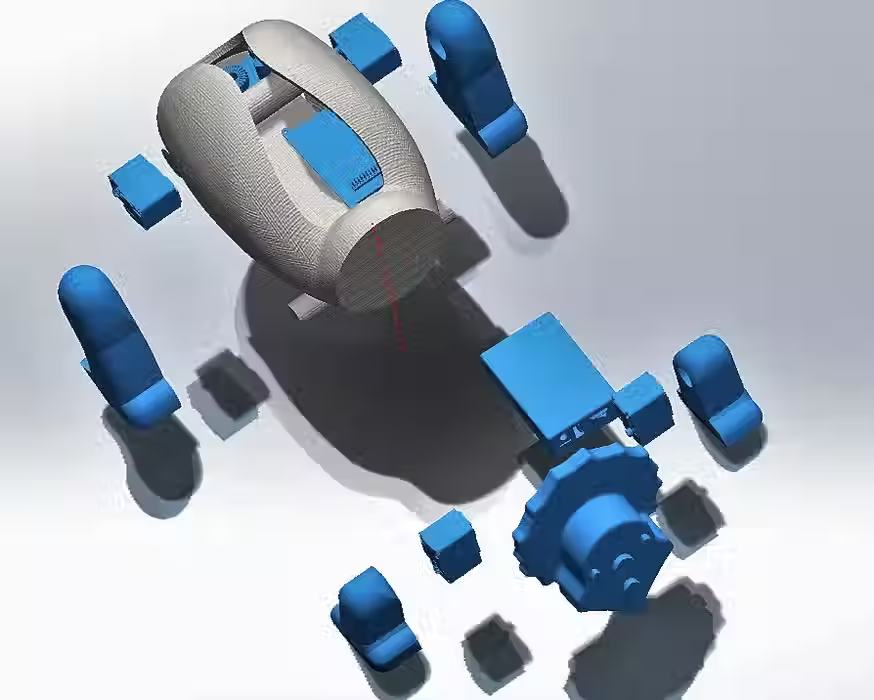
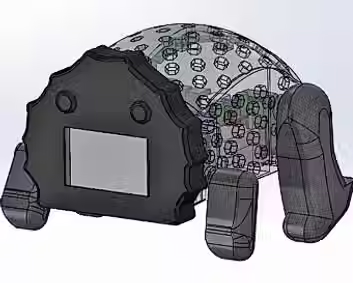
Render of internal components
Illustrative concept to demonstrate methods; parameters are intentionally generic. Any resemblance to real designs is coincidental. Content policy: T&Cs.
[09]
2025
Project
[Design]
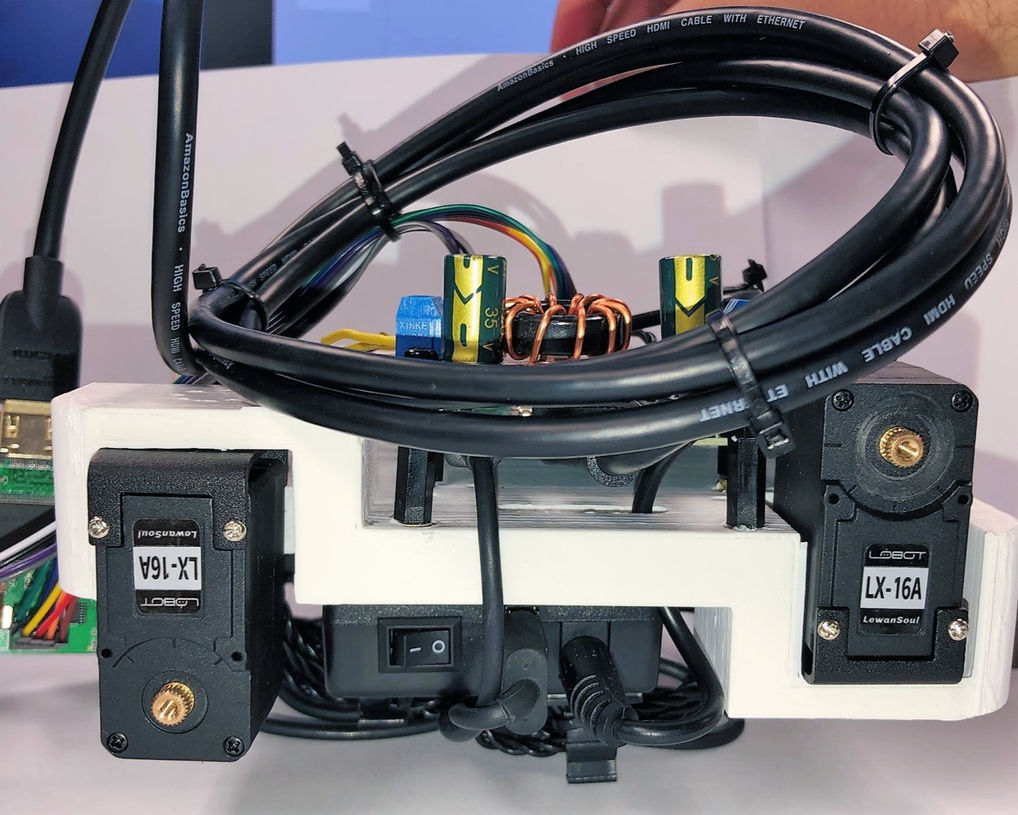
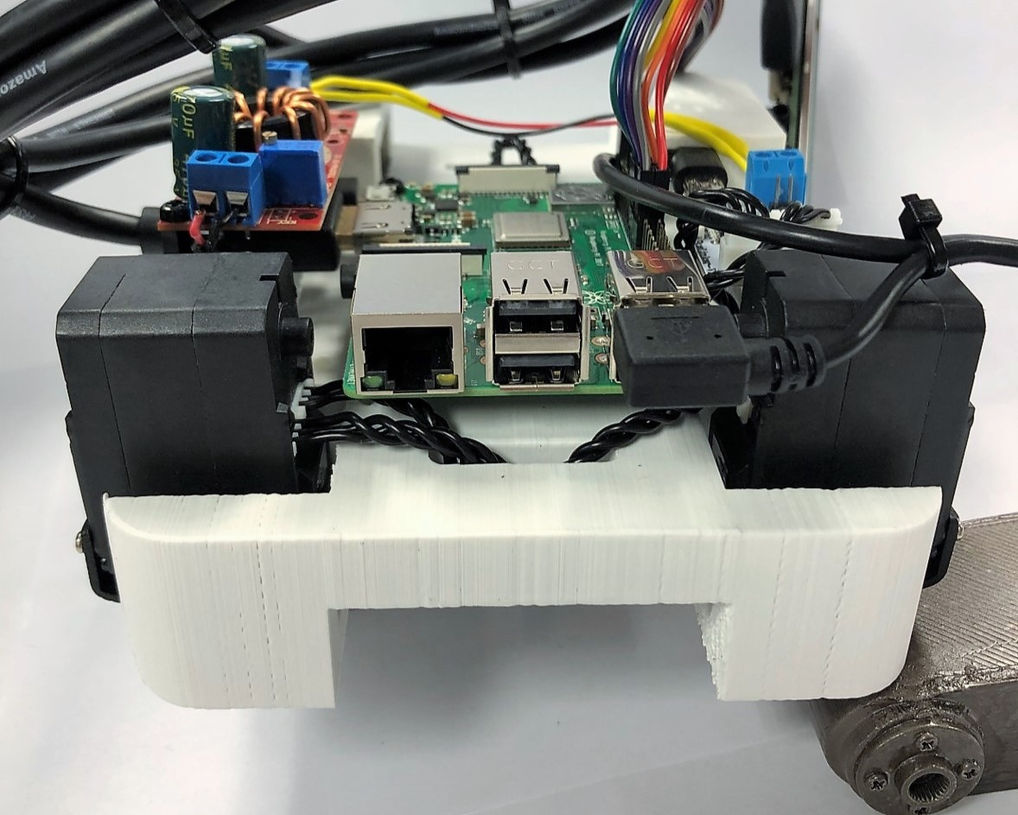
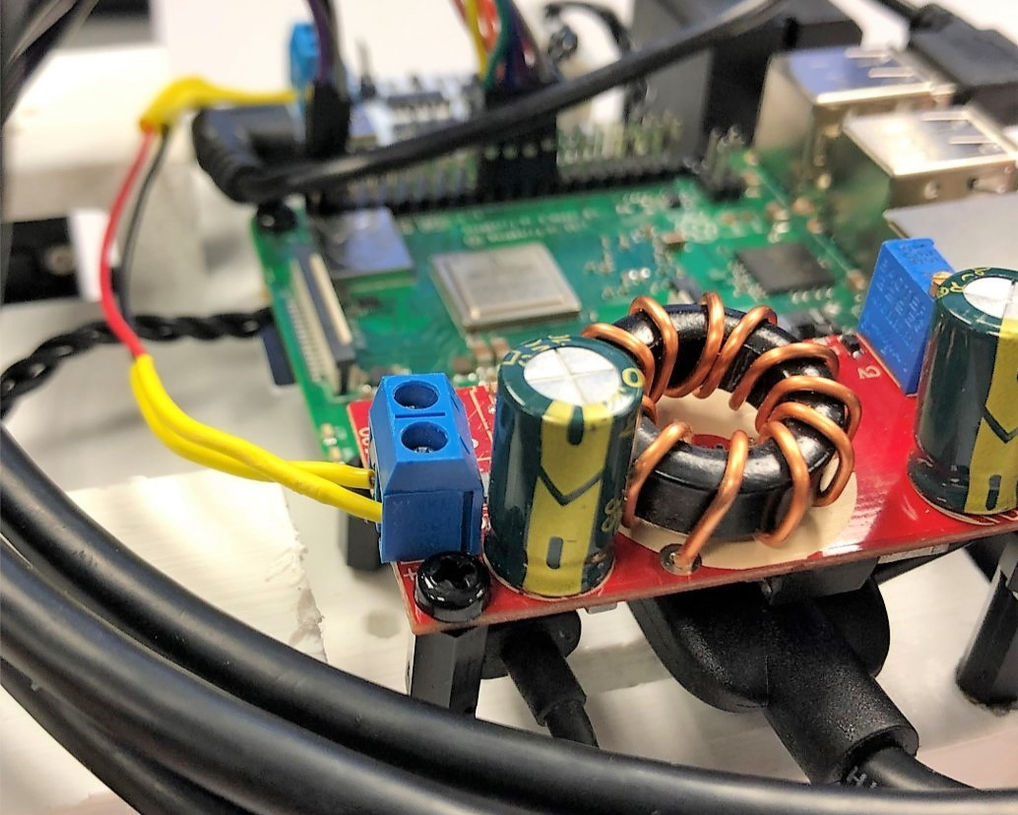
Internal Components
Illustrative concept to demonstrate methods; parameters are intentionally generic. Any resemblance to real designs is coincidental. Content policy: T&Cs.
[09]
2025
Project
[Design]

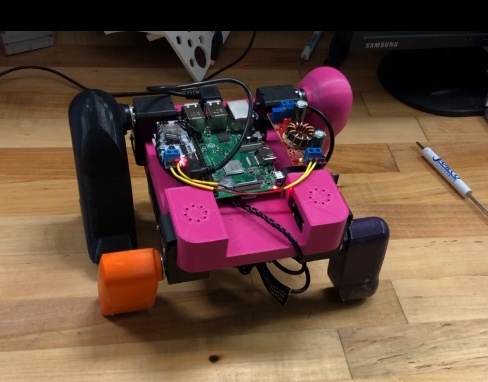
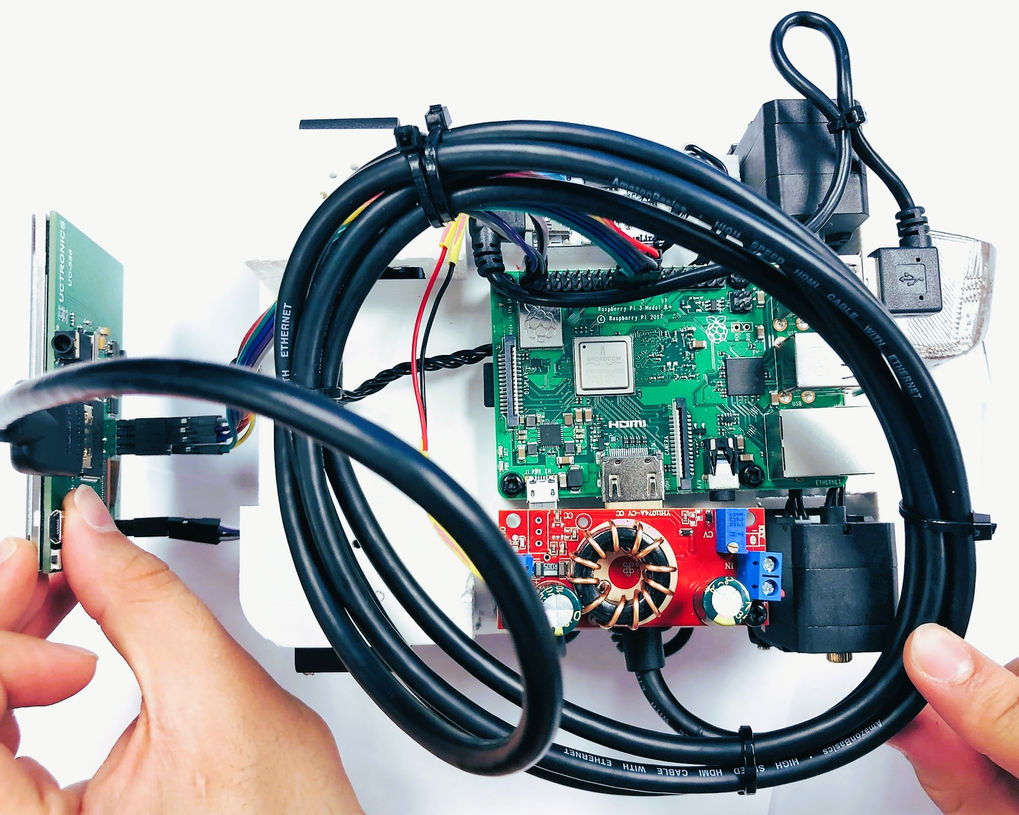
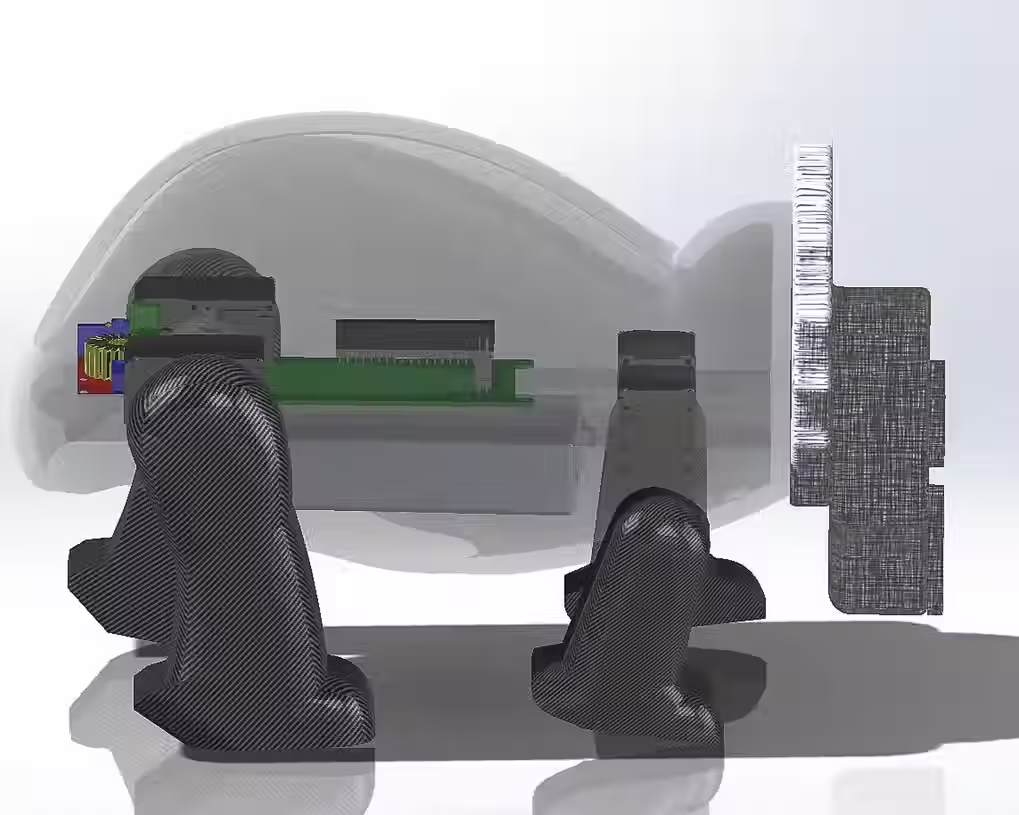
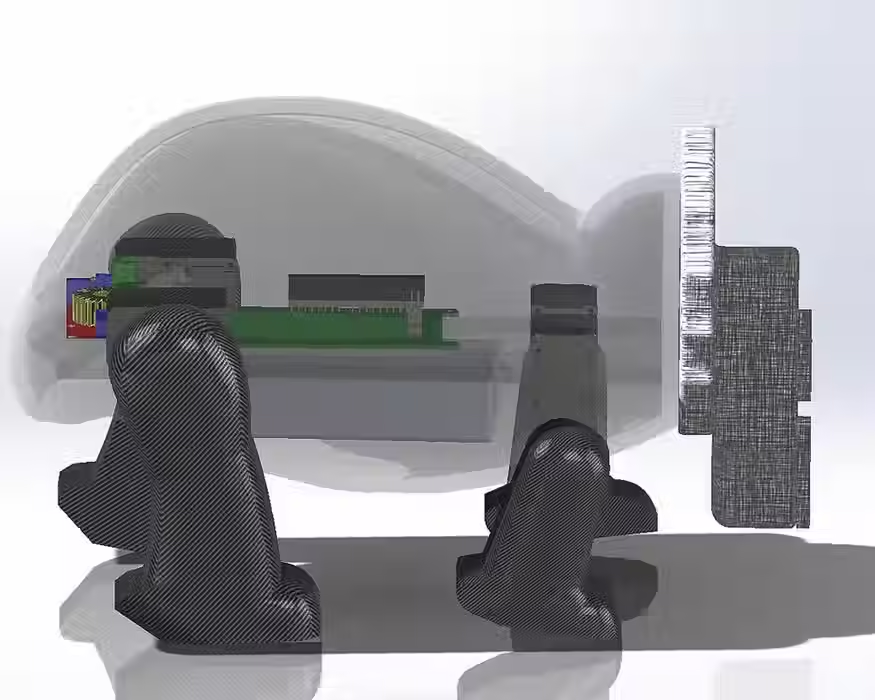
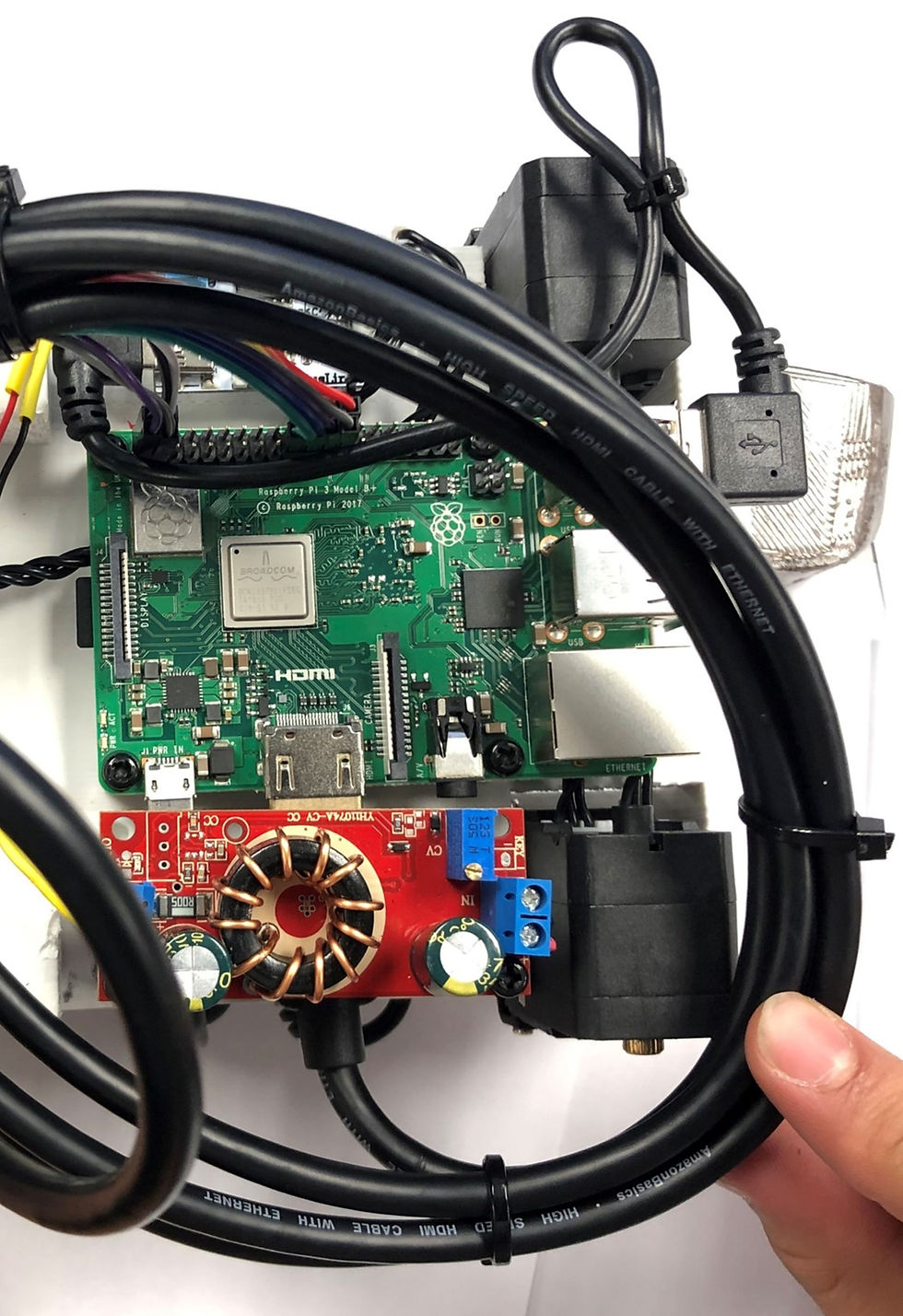
Internal Wirings of the Bot
Illustrative concept to demonstrate methods; parameters are intentionally generic. Any resemblance to real designs is coincidental. Content policy: T&Cs.
Quadra Dynamic Robot
[09]
2025
Project
[Design]
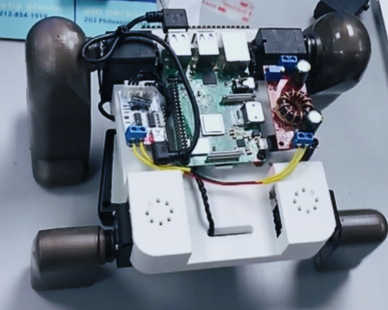
Range of Visal Facets and Variations of Project.
Illustrative concept to demonstrate methods; parameters are intentionally generic. Any resemblance to real designs is coincidental. Content policy: T&Cs.

Quadruped-Inspired Robot Design
Develop an autonomous, organically styled quadruped robot—modelled on triceratops morphology—that traverses 30 % of its body length per gait cycle.
Working Details
Phase 1: Concept Shortlisting – Generated multiple structural alternatives and shortlisted the optimum frame for strength‑to‑weight efficiency while preserving the triceratops‑inspired silhouette. Critical load paths and joint clearances were mapped to guarantee structural integrity during dynamic locomotion.
Phase 2: Lattice & CAD Optimisation – Employed Altair lattice optimisation to minimise mass yet maximise stiffness, then completed a full SolidWorks assembly that included motor mounts, cable routing, and sensor recesses. Gait kinematics and ABS stress fields were validated in simulation, confirming a target stride of 0.3 L cycle⁻¹ without yielding.
Phase 3: Rapid Prototyping & Electronics – 3D‑printed modular components on an Ultimaker 5.1 in ABS; individual servo IDs, an LCD touch interface, and a Python control stack were coded on a Raspberry Pi motherboard. Closed‑loop algorithms synchronised leg phasing for obstacle avoidance and bi‑directional path planning.
Phase 4: Assembly & Field Trials – Integrated power, Li‑Po packs, and sensor buses before final bolt‑up. Full‑system tests confirmed repeatable 30 % body‑length stride efficiency, stable autonomous walking, and seamless user control via ROS dashboards.

Tools and Skillset
Organic robotic structural design
Altair lattice optimisation & SolidWorks motion
nTopology joint‑weight reduction
Sensor integration & soldering
EAGLE PCB & cable management
Ultimaker 3D printing (STL workflow)
ROS & Python motion control
Li‑Po battery‑pack circuitry
GD&T analysis for moving joints